Pregnancy Glossary: A to Z Guide to Pregnancy Terminology
Chromosomal Abnormalities
Chromosomal abnormalities, alterations and aberrations are at the root of many inherited diseases and traits. Chromosomal abnormalities often give rise to birth defects and congenital conditions that may develop during an individual's lifetime. Examining the karyotype of chromosomes (karyotyping) in a sample of cells can allow detection of a chromosomal abnormality and counselling can then be offered to parents or families whose offspring are at risk of growing up with a genetic disorder.
Types of chromosomal abnormalityA chromosomal abnormality may be numerical or structural and examples are described below:
Numerical abnormalitiesThe normal human chromosome contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, giving a total of 46 chromosomes in each cell, called diploid cells. A normal sperm or egg cell contains only one half of these pairs and therefore 23 chromosomes. These cells are called haploid.
The euploid state describes when the number of chromosomes in each cell is some multiple of n, which may be 2n (46, diploid), 3n (69, triploid) 4n (92, tetraploid) and so on. When chromosomes are present in multiples beyond 4n, the term polyploid is used.
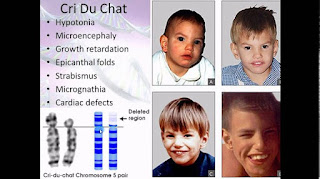
Aneuploidy refers to the presence of an extra chromosome or a missing chromosome and is the most common form of chromosomal abnormality. In the case of Down's syndrome or Trisomy 21, there is an additional copy of chromosome 21 and therefore 47 chromosomes. Turner's syndrome on the other hand arises from the absence of an X chromosome, meaning only 45 chromosomes are present.
Occasionally, aneuploid and regular diploid cells exist simultaneously and this is called mosaicism. The condition involves two or more different cell populations from a single fertilized egg. Mosaicism usually involves the sex chromosomes, although it can involve autosomal chromosomes.
In contrast to mosaicism, a condition called chimaerism occurs when different cell lines derived from more than one fertilized egg are involved.
Structural abnormalitiesStructural abnormalities occur when the chromosomal morphology is altered due to an unusual location of the centromere and therefore abnormal lengths of the chromosome's short (p) and long arm (q).
Some of the most common chromosomal abnormalities include:
Symptoms & Types
There are many different symptoms -- and several different types -- of bipolar disorder. The primary symptoms are dramatic and unpredictable mood swings. The types of bipolar disorder range from mild to severe.
Bipolar disorder can be sneaky. Infrequent episodes of mania can go undetected. Depression can overshadow other aspects of the illness. And substance abuse can further cloud the picture.
Bipolar disorder can be difficult to diagnose, but these tips may help you recognize the symptoms.
The primary symptoms of bipolar disorder are periods of elevated or irritable mood accompanied by dramatic increases in energy, activity, and fast thinking.
How to recognize the symptoms of mania and hypomania, part of the manic phases of bipolar disorder.
The dramatic mood episodes of bipolar disorder do not follow a predictable pattern.
There are several types of bipolar disorder; all involve episodes of depression and mania to a degree.
A person affected by bipolar I disorder has had at least one manic episode in their life. Most people with bipolar I disorder also suffer from episodes of depression.
In bipolar II disorder, the "up" moods never reach full-blown mania. These less-intense elevated moods are called hypomanic episodes.
In rapid cycling, a person with the disorder experiences four or more episodes of mania or depression in one year. This can occur at any point in the course of bipolar disorder.
A person with mixed bipolar episodes has symptoms of both mood "poles" -- mania and depression -- at the same time or in rapid sequence.
In cyclothymic disorder, moods swing between short periods of mild depression and mania.
The bipolar spectrum refers to conditions that include not only bipolar disorder but also other types of mental conditions that involve depression or mood swings.
Bipolar Disorder Resource Center
div { width: auto; } .Ad.Ad-141 {margin: 0 auto 3.75rem; max-width: 71.875rem; min-height: 8.25rem;} .Ad.Ad-141 > div { min-width: 728px; width: auto; } ]]>



Comments
Post a Comment