Blood Disorder Types, Symptoms, and Treatments
Blood Diseases
Do you know what is your blood made up of? There are several components of blood- red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma. Your blood majorly consists of plasma which is the liquid part and consists of protein and salts. Red blood cells work to supply oxygen to the tissues, white blood cells are important to fight infections and platelets help in clotting. When one or more parts of the blood get affected by blood diseases, your blood is unable to perform its core functions. In most cases, blood diseases are hereditary but there are several other reasons such as other diseases, deficiency of nutrients and side-effects of medications, that can cause a blood disease to occur.
What are the symptoms of a blood disease?
Symptoms of blood diseases are different from one another. It depends on what part of the blood is affected and how severe it has become. Let us tell you the general signs of a blood disease.
Symptoms of red blood cell diseases:
Symptoms of white blood cell diseases:
Symptoms of platelet diseases:
Blood Diseases Affecting Red Blood Cells
Anaemia: This is a very common blood disorder that is caused when the number of red blood cells becomes too low in the blood. Mildly anaemic people don't show significant symptoms but severe anaemic people may experience a problem in breathing, fatigue and pale skin.
Iron-deficiency anaemia: You must have heard that iron is very important for the body. It is because it makes red blood cells. When you don't consume an adequate amount of iron, it causes iron-deficiency. Menstruating women should have iron to combat red blood cell loss during periods.
Chronic Disease Anaemia: People who have chronic diseases like kidney diseases are highly likely to develop anaemia. This doesn't require treatment as this can be managed by a synthetic hormone named Epogen or Procrit to increase the production of red blood cells. Only some patients may require blood transfusions.
Pernicious anemia or vitamin B12 deficiency: If you are not consuming enough vitamin B12 or your body is unable to absorb this vitamin from your diet, this anaemia may be caused. The common cause of this condition is an autoimmune disease.
Aplastic anemia: In this disease, there is a problem with the bone marrow as it doesn't produce enough red blood cells. Hepatitis, pregnancy, HIV, chemotherapy medications and side-effects to any drug may be causing this condition. If the condition is not treated with medications and blood transfusions, the patient may need a bone marrow transplant.
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia: When the red blood cells are destroyed due to an overactive immune system, it causes hemolytic anaemia. Immune-suppressing medicines can help in controlling this condition.
Thalassemia: This is a chronic blood disease wherein the patients are administered blood transfusions regularly.
Polycythemia vera: Excess of red blood cells is also injurious to health. If the body produces too many red blood cells, it may cause unnecessary blood clots.
Malaria: Not many people know but malaria is also a red blood cell disease where the mosquito carrying the parasite bites a person and injects the parasite into the blood. This causes infection in red blood cells and leading to numerous symptoms.
Blood Diseases Affecting White Blood Cells
Lymphoma: This is a kind of blood cancer where a white blood cell named lymphoma becomes malignant and starts to multiply and spread abnormally. The two types of this cancer are- Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy can reduce the damage and cure this cancer condition.
Leukaemia: This is another blood cancer where white blood cells inside the bone marrow become malignant. Leukaemia may be slow progressing or severe and the best ways to combat this condition are bone marrow transplant(stem cell transplant) and chemotherapy.
Multiple myeloma: This is another blood cancer where plasma cell becomes cancerous and releases a dangerous substance that can cause damage to organs. There is no cure for this condition but treatments like chemotherapy and stem cell transplant can extend the life span of the patient.
Myelodysplastic syndrome: This is a slowly-progressing syndrome that is a blood cancer. This can progress into acute leukaemia.
Blood Diseases Affecting Platelets
Thrombocytopenia: When the number or platelets in the blood are very low, thrombocytopenia condition can be caused. This disorder is characterised by abnormal bleeding.
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: This thrombocytopenia condition is induced by heparin which is a blood thinner that helps in the prevention of blood clotting. This can cause a low platelet count. Abnormal bleeding, abnormal bruising and red spots on the skin are symptoms of this condition.
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: This is a very rare condition where clotting occurs in the blood vessels leading to a drop in the platelet count.
Primary thrombocythemia or Essential thrombocytosis: In this condition, the body produces excess platelets due to either reason but these don't use up properly leading to bleeding and excessive blood clotting.
Blood Diseases Affecting Blood Plasma
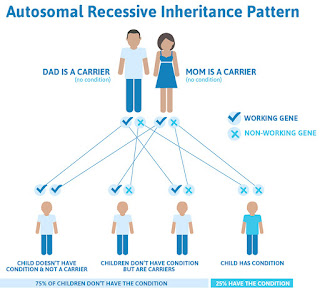
Haemophilia: This is a deficiency in genes where some proteins trigger the blood to clot. Depending on the severity of the condition, there are different types of Haemophilia.
Hypercoaguable state: This is a condition where the blood easily clots and in most cases, this condition goes unnoticed and undiagnosed. Some people may suffer from this condition throughout their lives and some have a severe form of this condition where they may need to take blood thinning medicines daily to combat the situation.
Deep venous thrombosis: In this blood disorder, blood clotting occurs in the deep vein which is mostly in the leg. This disease can travel to your vital organs where it may also cause a pulmonary embolism.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC): This is a blood disease that causes unnecessary bleeding and small blood clots in the entire body. Several conditions like pregnancy complications, recent surgery and severe infections can lead to this condition.
von Willebrand disease: In this blood disorder, the body either produces too little or too high von Willebrand factor protein. This protein is essential in blood clotting. In most cases, this disease is inherited but sadly, it doesn't have visible symptoms.
Heart Disease: Types, Causes, And Symptoms
There are many types of heart disease, and each one has its own symptoms and treatment. For some, lifestyle changes and medicine can make a huge difference in improving your health. For others, you may need surgery to make your ticker work well again.
Find out about some of the common types of heart disease and how to prevent them as well as how they're treated.
CAD is the most common heart problem. With CAD, you may get blockages in your coronary arteries -- the vessels that supply blood to your heart. That can lead to a decrease in the flow of blood to your heart muscle, keeping it from getting the oxygen it needs. The disease usually starts as a result of atherosclerosis, a condition sometimes called hardening of the arteries.
Coronary heart disease can give you pain in your chest, called angina, or lead to a heart attack.
Some things that may put you at a higher risk of coronary artery disease are:
When you have an arrhythmia, your heart has an irregular beating pattern. Serious arrhythmias often develop from other heart problems but may also happen on their own.
With heart failure, your heart doesn't pump blood as well as it should to meet your body's needs. It is usually caused by coronary artery disease, but it can also happen because you have thyroid disease, high blood pressure, heart muscle disease (cardiomyopathy), or certain other conditions.
Your heart has four valves that open and close to direct blood flow between your heart's four chambers, the lungs, and blood vessels. An abnormality could make it hard for a valve to open and close the right way. When that happens, your blood flow could be blocked or blood can leak. Your valve may not open and close right.
The causes of heart valve problems include infections such as rheumatic fever, congenital heart disease, high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, or as a result of a heart attack.
Diseases of the heart valves include:
Any disease of the pericardium, the sac that surrounds your heart, is called a pericardial disease. One of the more common diseases is pericarditis or inflammation of the pericardium.
It's usually caused by an infection with a virus, inflammatory diseases such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, or injury to your pericardium. Pericarditis often follows open heart surgery.
Cardiomyopathy is a disease of your heart muscle, or myocardium. It gets stretched, thickened, or stiff. Your heart may get too weak to pump well.
There are many possible causes of the disease, including genetic heart conditions, reactions to certain drugs or toxins (such as alcohol), and infections from a virus. Sometimes, chemotherapy causes cardiomyopathy. Many times, doctors can't find the exact cause.
Congenital heart disease happens when something goes wrong while the heart is forming in a baby that's still in the womb. The heart abnormality sometimes leads to problems right after birth, but other times there aren't any symptoms until you become an adult.
Septal abnormalities are among the most common congenital heart problems. These are holes in the wall that separates the left and right sides of your heart. You can get a procedure to patch the hole.
Another type of abnormality is called pulmonary stenosis. A narrow valve causes a decrease in the flow of blood to your lungs. A procedure or surgery can open or replace the valve.
In some babies, a small blood vessel known as the ductus arteriosus doesn't close up at birth as it should. When this happens, some blood leaks back into the pulmonary artery, which puts strain on your heart. Doctors can treat this with surgery or a procedure or sometimes with medication.
Anxiety: The Causes, Symptoms And Types
by CHARLOTTE HARDING, femail.Co.Uk
A staggering 10 million people in the UK suffer from anxiety problems.
Here, as part of our week-long look at mental health we present a guide to the causes, symptoms and different types of anxiety disorders.
Click on the link at the bottom of the page for our guide to treatments for anxiety, myths and facts about the illness and your questions answered by an expert.
THE CAUSES
Anxiety disorders can be triggered by many causes, for example a major upheaval like moving house, a marriage break up or having a baby.
Something distressing that has happened in the past may be to blame if you were not able to deal with the emotions at the time. This is because you may fear the same thing happening again in case it stirs up the same sorts of feelings.
Other sufferers worry about the future. If we feel out of control of different aspects of out lives, we can start to feel anxious about the future and possible events beyond our control.
Other people may have learned to feel anxious from an early age because they have been taught to view the world as a hostile and fearful place.
Poor eating and drinking habits can also cause anxiety. Excess caffeine, sugar, poor diet, drug misuse, exhaustion, stress and the side-effects of certain medication can also cause the condition.
Even the stresses of everyday life can be triggers, although some sufferers are never able to identify a specific cause.
The condition can appear at any age but most often it begins in the late 20s and strikes people from any walk of life. Increasingly teachers, nurses and college students are turning to support groups for help. Twice as many women suffer as men, although it is not clear why.
THE SYMPTOMS
Commonly, serious anxiety starts with a panic attack - a very frightening experience because it seems to come out of the blue. Common symptoms are sweating, a racing heart, palpitations, or rapid breathing. Your hands may tingle or feel numb and you might feel flushed or chilled.
Other symptoms include feelings you are out of control or going crazy, a fear of dying and terror.
These changes are caused by an increase in adrenaline, the chemical which is released by your body to help you get ready to deal with danger.
Many people with severe anxiety have feelings that strike suddenly and repeatedly without warning and they often develop intense anxiety between episodes, worrying when and where the next one will strike.
Attacks can happen any time, even during sleep and while most last for an average of a couple of minutes, occasionally they can go on for up to 10 minutes or, in rare cases, more than an hour.
Anxiety which continues for a long time can have a serious effect on people's lives. Sufferers often begin to avoid everyday activities such as shopping, driving or in some cases even leaving the house or their bed.
THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF ANXIETY DISORDERS
Agoraphobia: This is the most common type of anxiety disorder in the UK - there are a staggering five million sufferers. This is a very broad problem which often begins with sufferers having panic attacks when they are away from home.
The sufferer may start to avoid the place where the initial panic attack took place, but often finds the attacks keep occurring wherever they are so gradually become too frightened to leave their home at all.
Phobias: A specific phobia is a fear of a particular object or place, which is so severe that it affects your way of life. It is possible to develop a phobia for almost anything, but some of the most common phobias are fear of heights, fear of spiders or mice, fear of enclosed spaces (known as claustrophobia) and fear of blood or injections. There are four million phobia sufferers in the UK.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder: There are two million people in the UK with obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD). Sufferers find that certain words or ideas keep coming into their minds automatically. This makes them feel very anxious, particularly if the thoughts are nasty, unpleasant or frightening.
For example, some people have repeated thoughts about germs causing disease or death. In order to cope with the anxiety they start to do things over and over again to get rid of the thoughts, such as washing their hands every few minutes, or reciting numbers.
Social phobia: There are around a million suffers of social phobia in Britain. Those affected are extremely anxious about what other people will think of them, or how they will be judged by other people. As a result they may have great difficulty in social situations, such as eating or drinking in the presence of other people.
General anxiety disorder: This makes the sufferer feel anxious and worried, irrespective of the situation they find themselves in. Symptoms vary from a mild feeling of anxiety to acute fear, similar to that experienced by a phobia sufferer. It is not known how many sufferers there are in the UK.
Click on the links below to read about the treatments for anxiety and much more.
{"status":"error","code":"499","payload":"Asset id not found: readcomments comments with assetId=131201, assetTypeId=1"}
Comments
Post a Comment